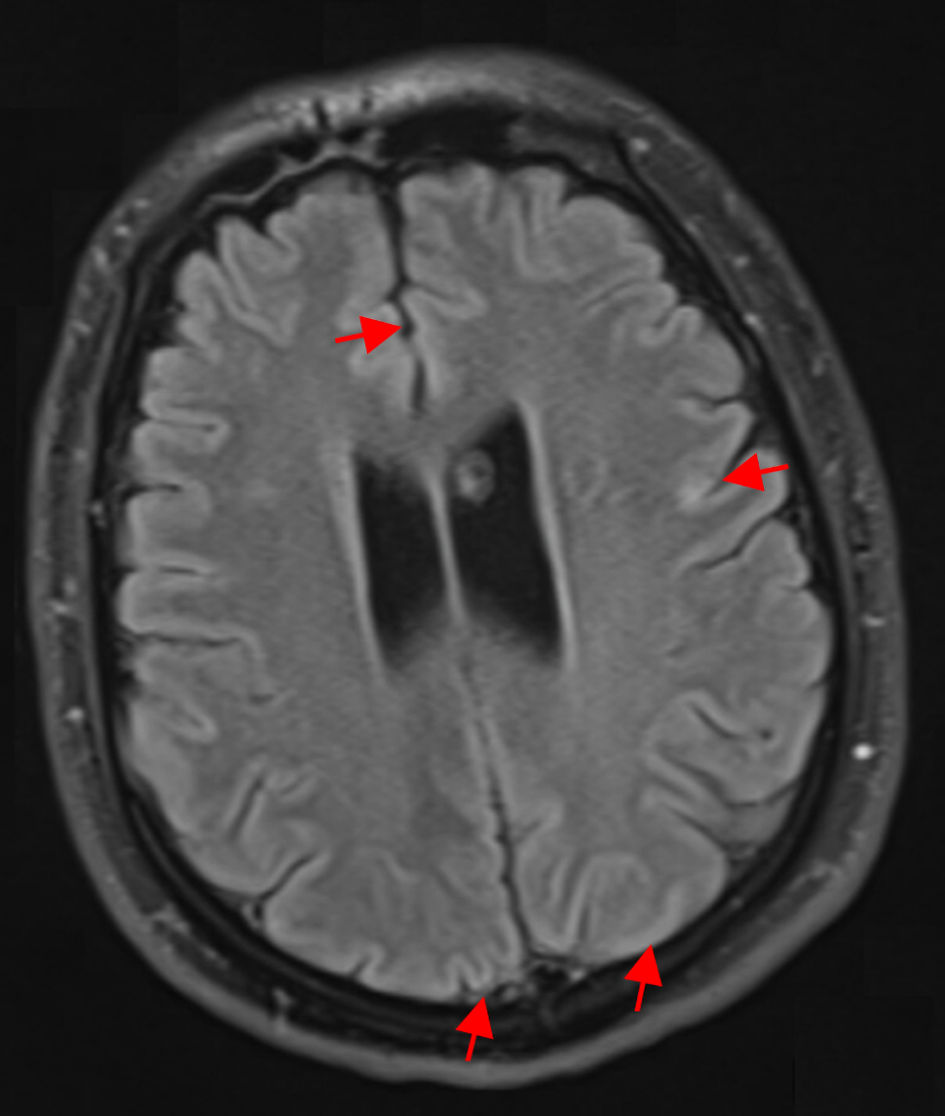
Figure 1. Axial FLAIR MRI without contrast at the level of the temporal lobes, demonstrating absence of the expected mesial temporal hyperintensities typically seen in HSV-1 encephalitis. There is curvilinear diffusion hyperintensity in the frontal and parietal cerebral cortex (red arrows). Both hippocampi, amygdalae, and insular cortices maintain normal signal intensity and grey-white differentiation. This lack of medial temporal FLAIR hyperintensity is atypical for HSV-1 encephalitis, which classically presents with unilateral or bilateral temporal lobe FLAIR hyperintensities and edema. FLAIR: fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; HSV-1: herpes simplex virus type 1.
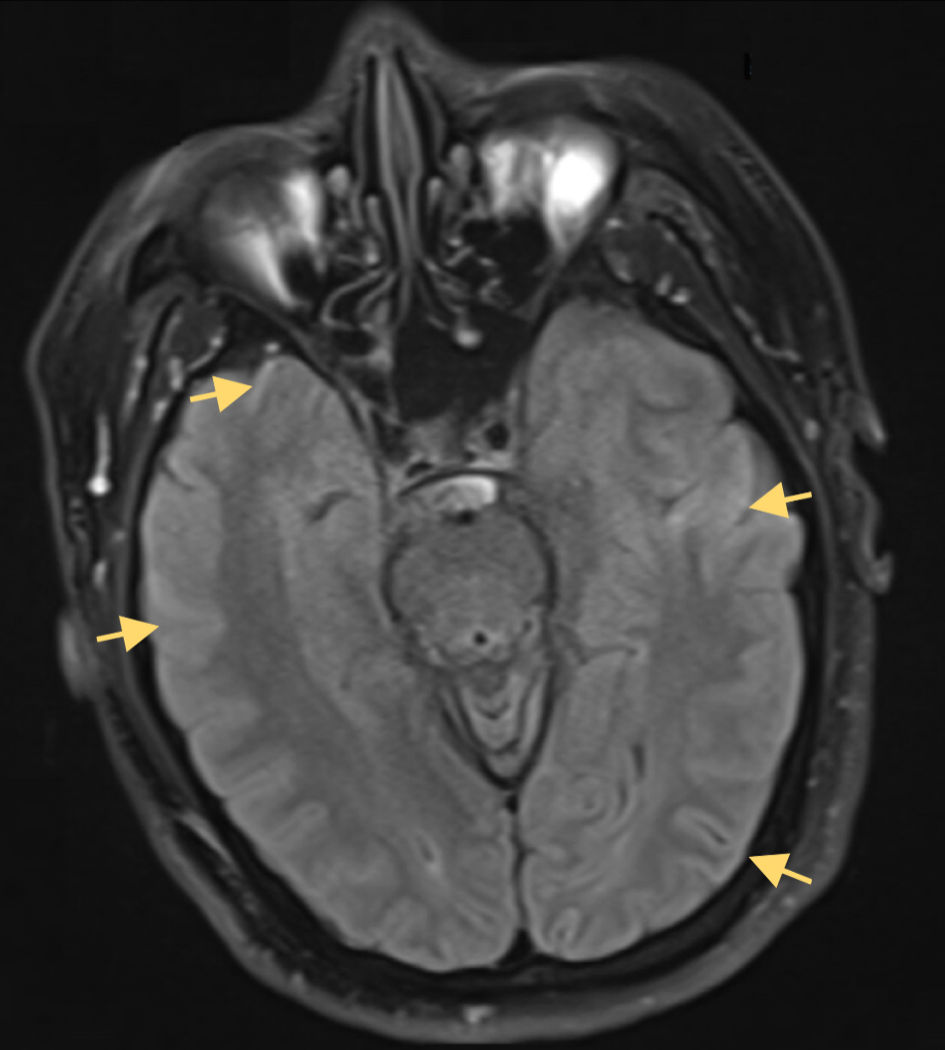
Figure 2. Axial DWI MRI without contrast of the brain demonstrating cortical ribboning curvilinear diffusion hyperintensity along the cerebral cortex in the temporal and parietal lobes (yellow arrows). The corresponding FLAIR sequence (Fig. 1) also showed cortical hyperintensities. No abnormal diffusion or signal is noted in the medial temporal lobes or insula, which is atypical for HSV-1 encephalitis. Classically, HSV-1 MRI lesions involve the mesial temporal and inferior frontal regions; in this case, the cortical ribboning pattern indicates a more diffuse cortical involvement and can be seen in encephalitic processes but is nonspecific. FLAIR: fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; DWI: diffusion-weighted imaging; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; HSV-1: herpes simplex virus type 1.

