Molecular Signaling Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease and Their Therapeutic Implications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jnr869Keywords:
Alzheimer’s disease, Signaling pathway, Therapeutic target, Multi-target, NeuropharmacologyAbstract
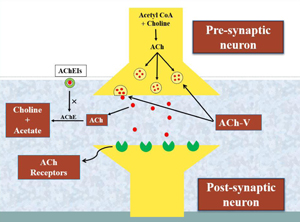
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) poses significant health challenges for the elderly due to its complex origins and heterogeneous etiology. Currently, there are no medications specifically aimed at halting its progression through any preventive signaling mechanism. Therefore, there is a pressing need to explore alternative pathways that could guide researchers towards new avenues in drug development for managing AD sustainability. This article is the first to simultaneously review several potential signaling pathways that were previously reported as individual signaling conduits in AD. Through meticulous analysis, we assess the pathophysiological roles of these pathways in AD. Extensive literature searches across databases including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, ResearchGate, Google Scholar, X-Mol, EBSCO, Loop, and Google, encompassing both research articles and highly cited reviews, were conducted. In addition to the cholinergic and N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate signaling pathways, we have observed four other less-explored, but promising molecular pathways relevant to AD onset and progression. We delved into the detailed signaling mechanisms of these pathways, spanning from preclinical to clinical studies. Remarkably, each pathway demonstrates distinct molecular signaling patterns and offers diverse perspectives on AD treatment. This review highlights six pivotal signaling pathways that may hold promise as future targeting pathways in managing AD.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







